Element Biosciences gave a webinar to present their latest offerings in Multi-Omics with their Teton Atlas product line.
Here are my highlights
We want to do Multiomics, but we want this to be all coherent and without having to buy N number of different instruments.
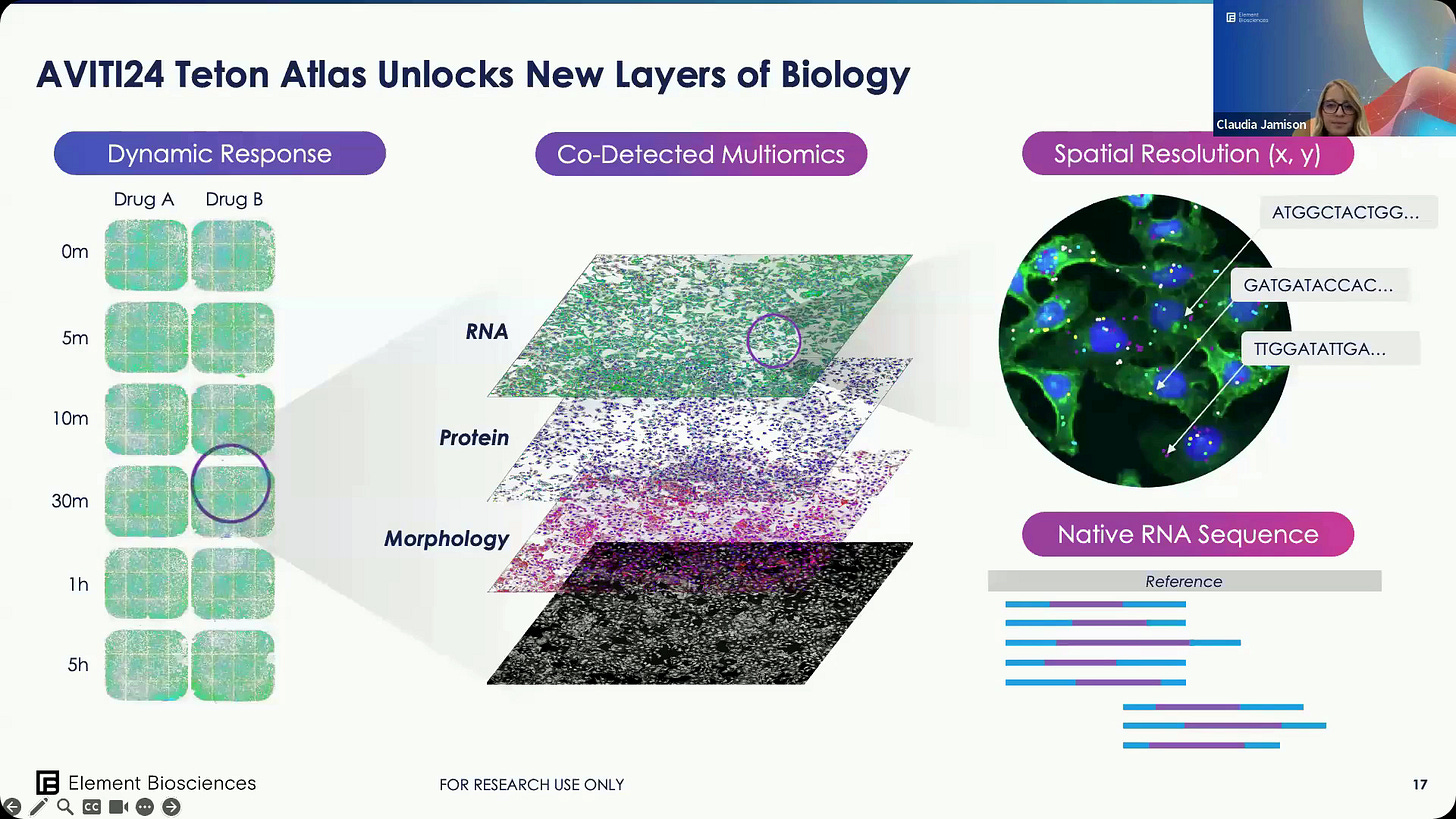
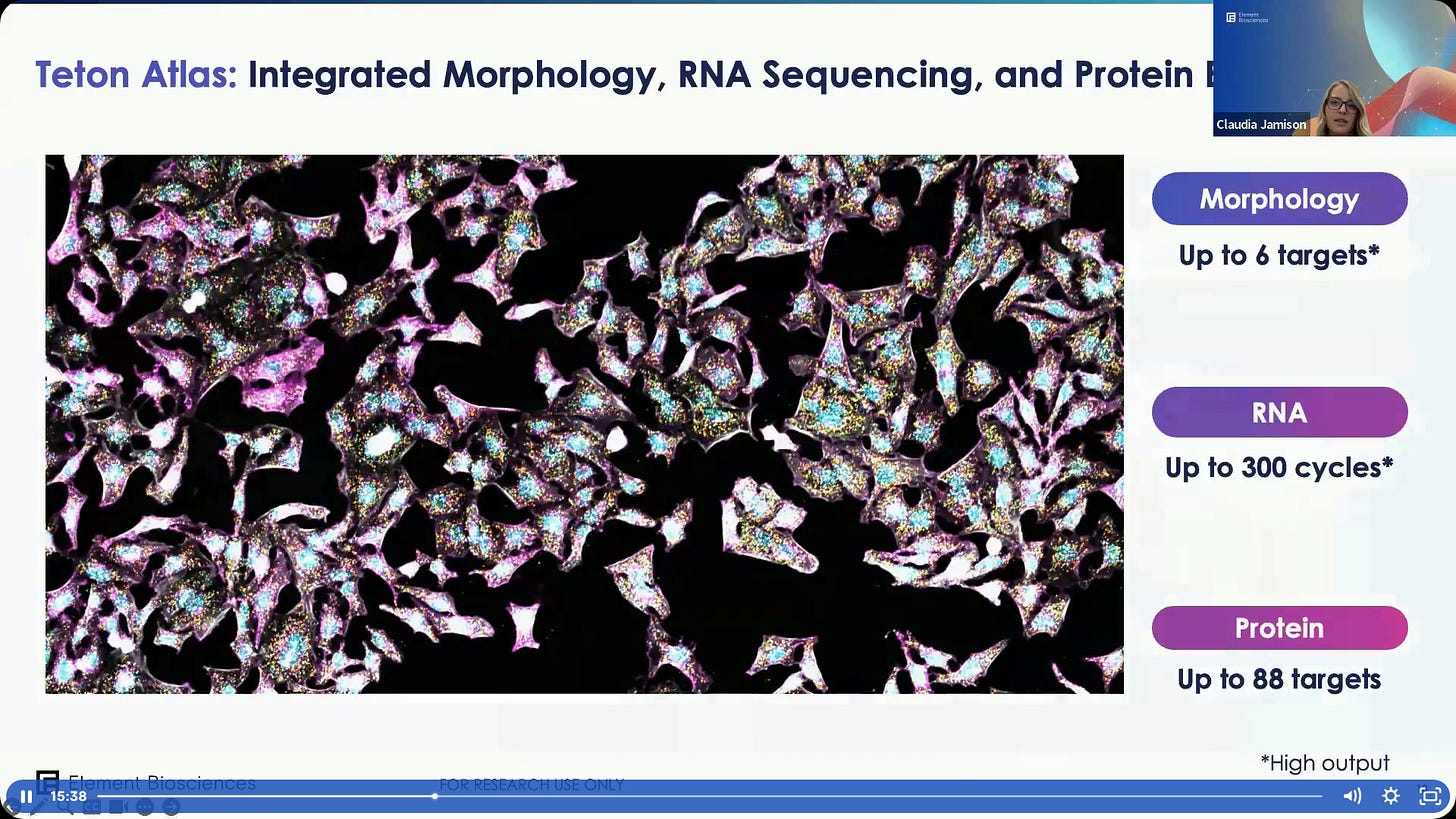
AVITI23 Teton: multiple samples can be queried in a simple run at the RNA, Protein and Morphology level.
The holy grail: delivering sample to insight with no library prep. The goal is to load the biological sample into the Element Bio flowcell, no preps needed.
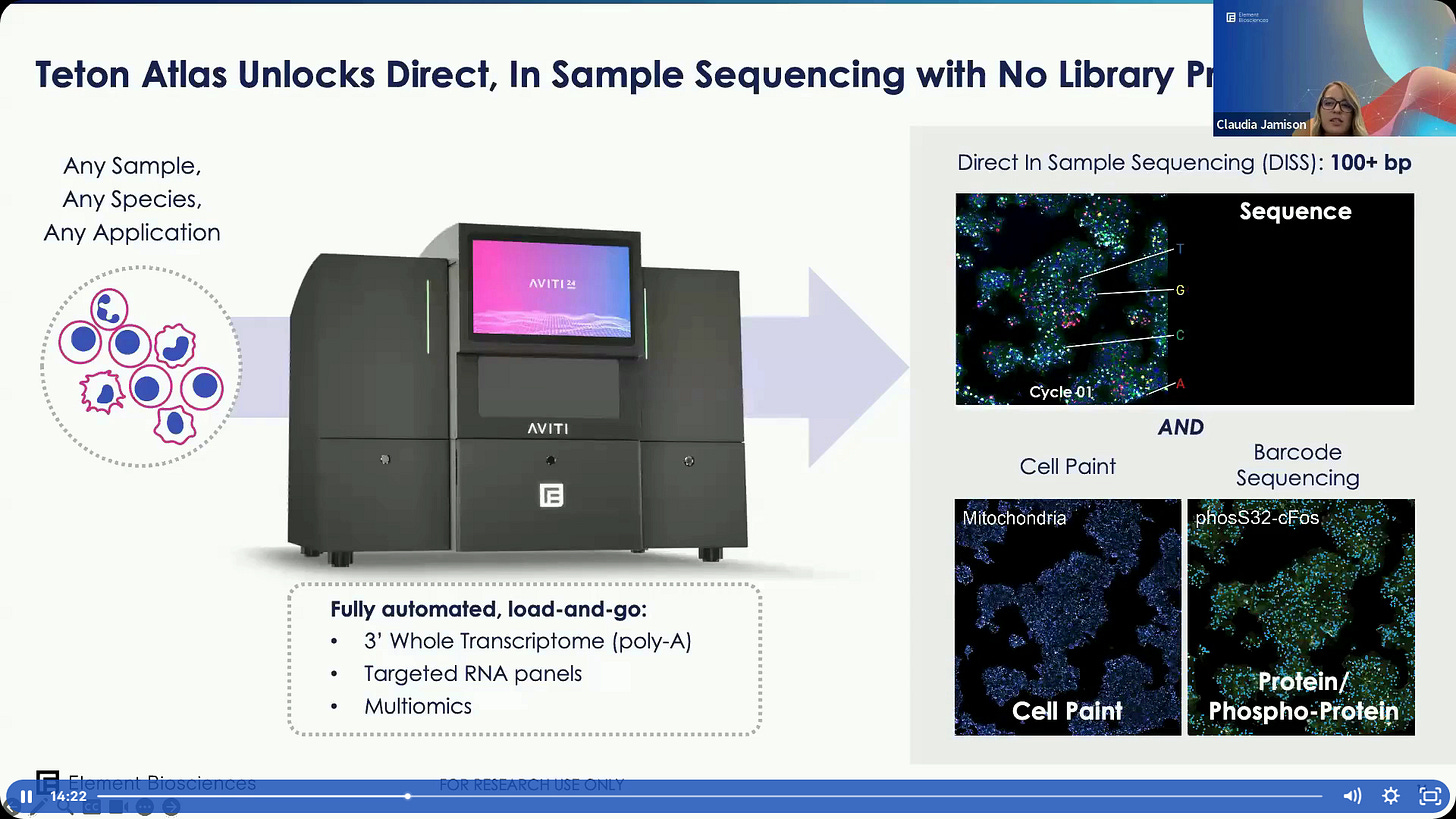
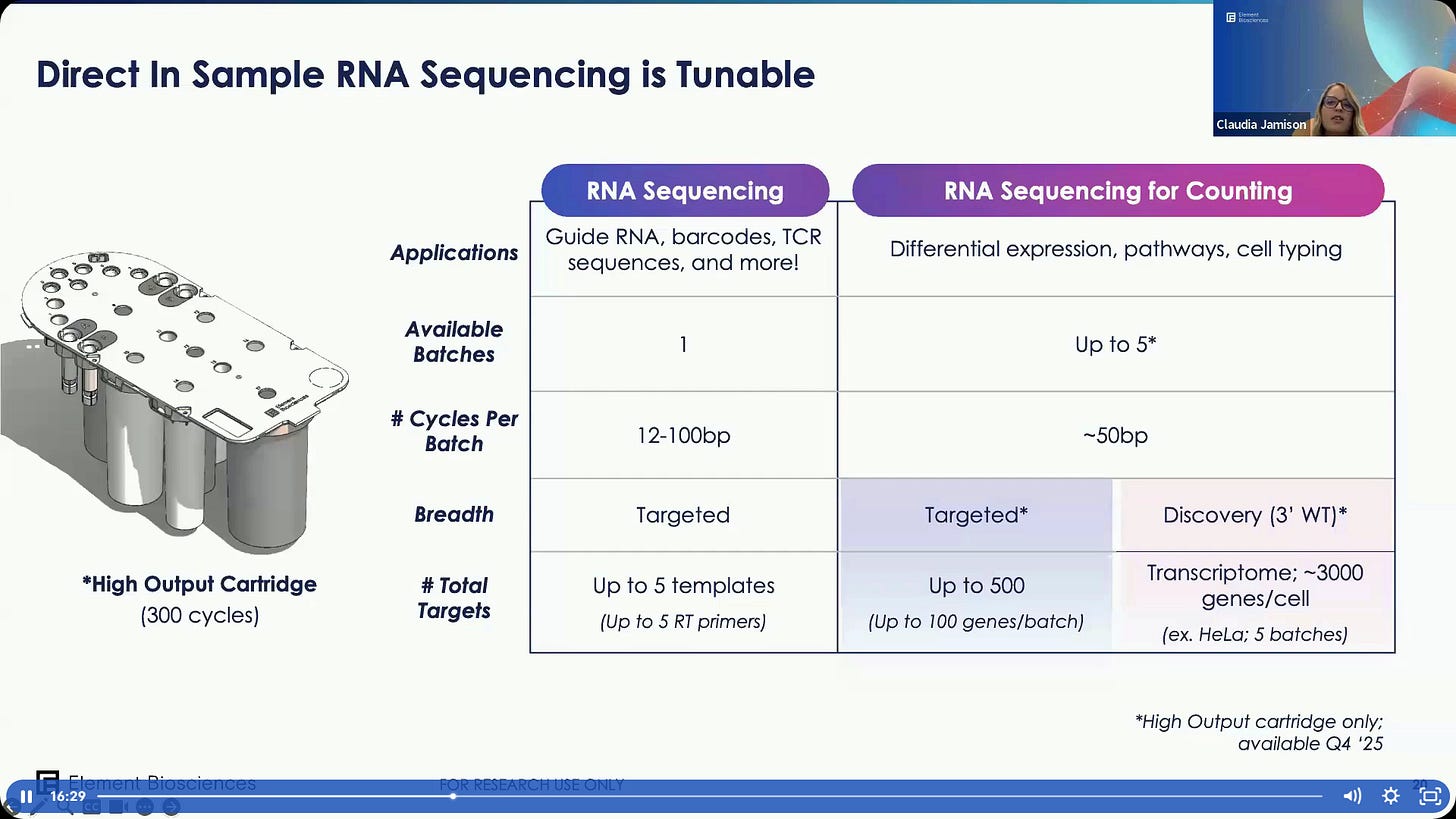
The new Teton Atlas, it can do RNA sequencing of up to 100bp, coming August 2025.
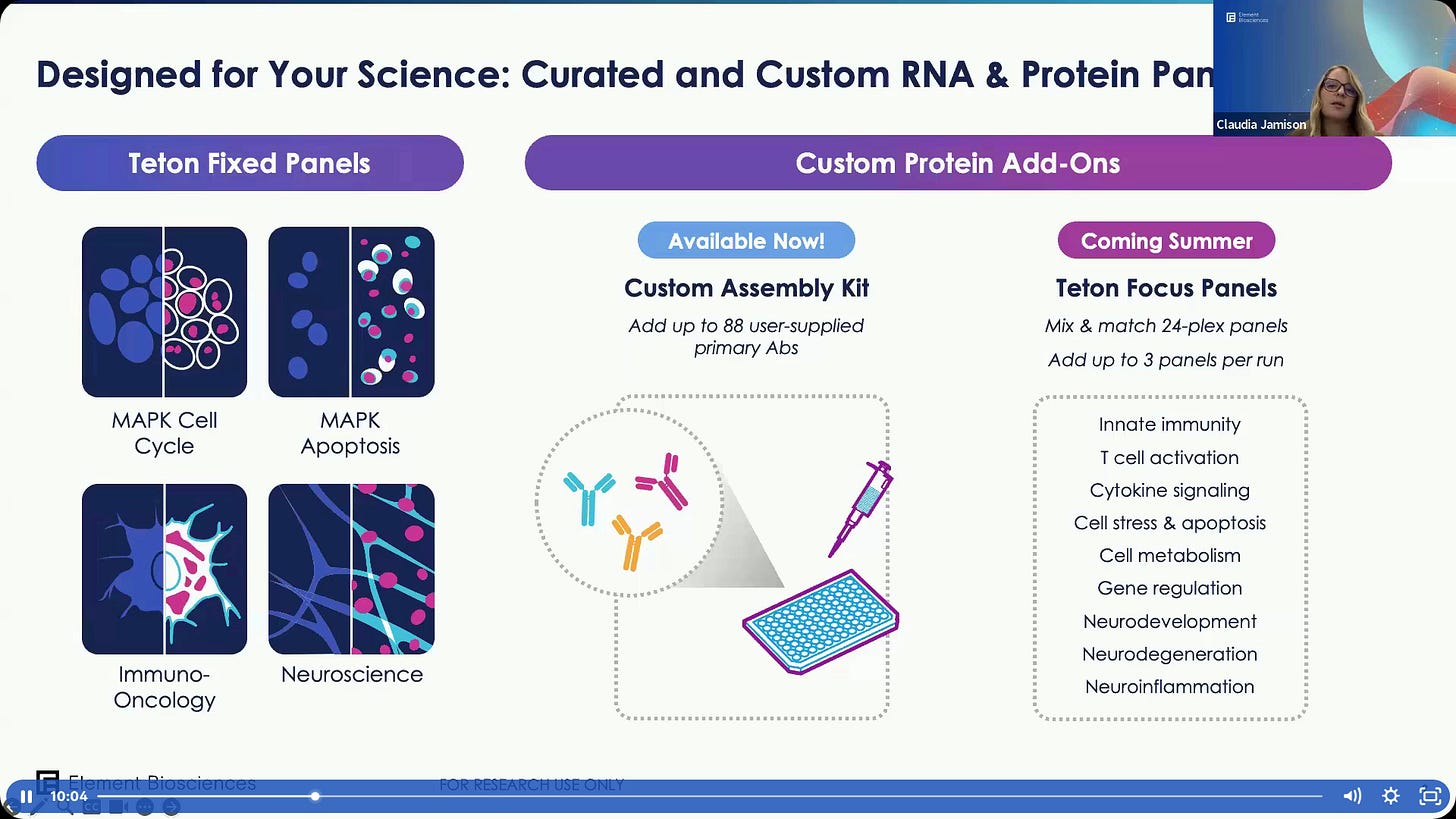
Some example panels already available in the Teton product.
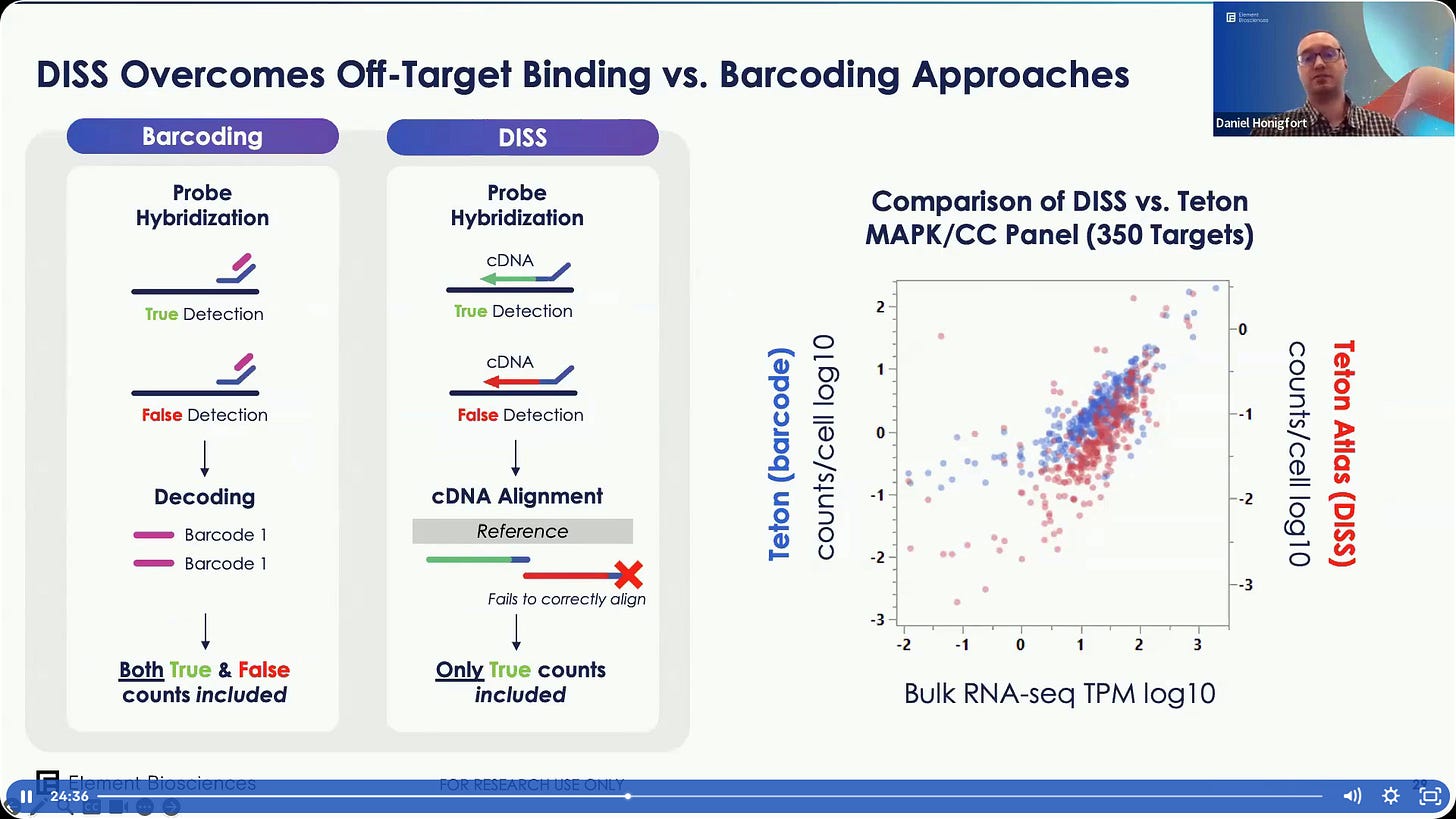
How does it work? Avidity-based chemistry, like the NGS sequencing part, probes attached to unique barcodes, segregating in batches of sequential sequencing. This avoids the issue of ‘optical crowding’ often observed in imaging-based methods.
There is a biorxiv preprint on how this works.
Another example: EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in Lung Cancer, here 350x RNA + 55x Protein + 6x Cell Paint.
All done in 2 days, including cell culture time. Details in the preprint.
Now diving into the new Teton Atlas. Some examples of where Direct In Sample Sequencing (DISS) is useful.
The main difference with Teton is that Teton Atlas can now do reads of 100bp+.
This means we can now do Native RNA Sequence.
There will also be a High Output version later on with up to 300 cycles of RNA DISS (although later on it says it’s only 100bp).
There are two cartridge configurations: Low Output and High Output, the later in late 2025.
Some examples of use. One can use RNA Sequencing for Counting applications, in which case 50bp is usually enough.
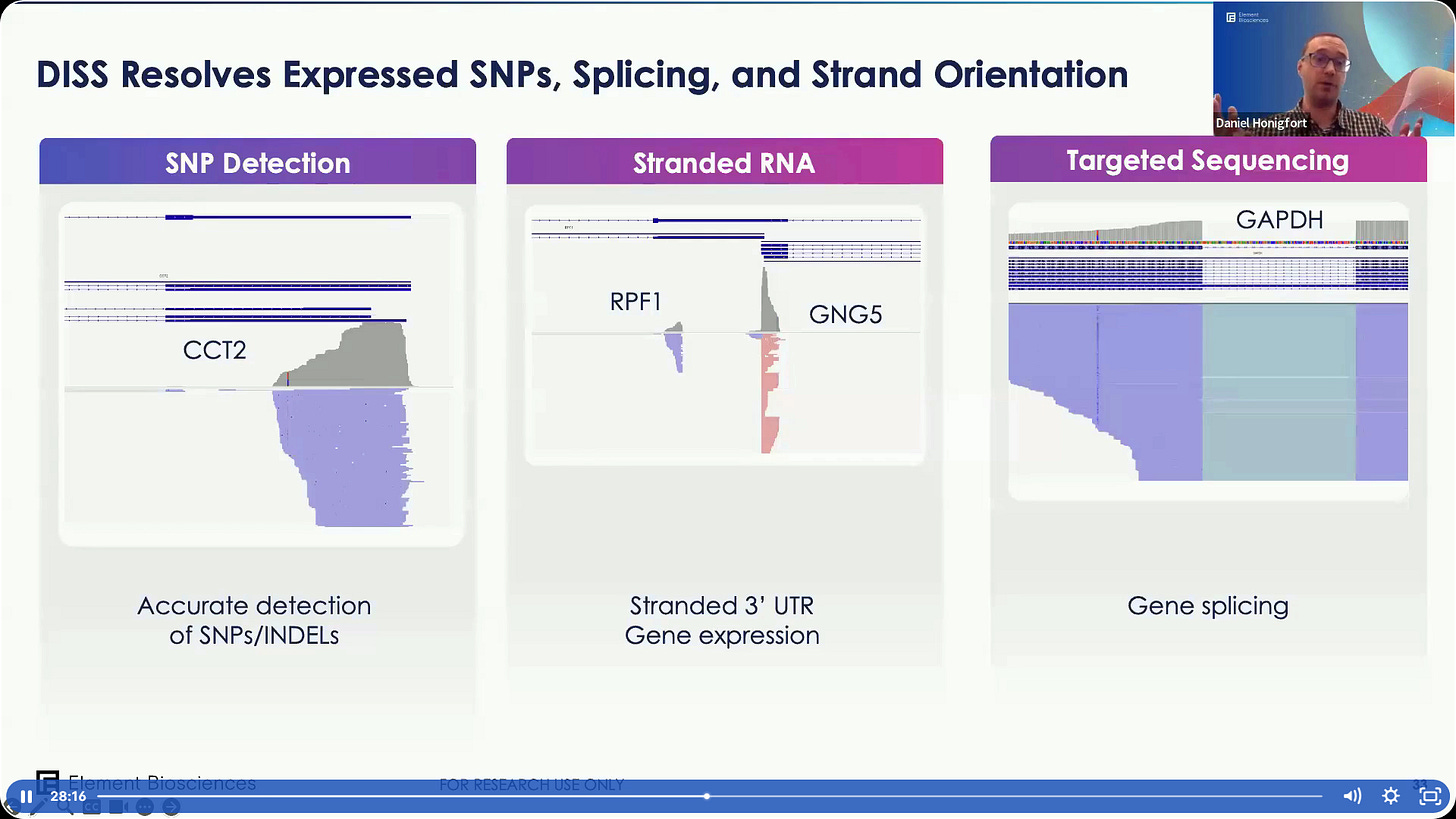
Some examples on using this Direct In Sample Sequencing. One example of a SNP in a transcript with exon splicing downstream, another example with the UTR regions of a gene.
The system is Fully Programmable by the Users. The different Modules are dropped-in by the user depending on the design.
An example below on how to design these using the website. Here describing a CRISPR Optical Pooled Screen scaffold set, which will be de novo sequenced with DISS.
Once that custom workflow is built, the primary analysis will do cell segmentation and morphology assessment, protein assignment and localization and base calling.
All the output from the run such as Cells2Stats (FASTQs), Read Alignment and Cell Assignment, CytoCanvas, now working on cell montages.
A summary of Teton Atlas.
Now for more details on how the DISS Chemistry works.
It works either as poly-T 3’ Transcriptome sequencing or targetted sequencing via probe hybridization. Same chemistry as the AVITI NGS sequencing on glass flowcells.
The probes are single-sided oligos, here showing how the software will design the RT Primer and Sequencing Primer, with flexibility for the user to order their own oligos.
Given that we are sequencing the molecules where the probe lands, it’s not prone to false positives like methods that don’t do actual sequencing (e.g. NanoString CosMx or 10X Genomics Xenium).
The sensitivity angle in Teton Atlas. The high output cartridge is up to 300 cycles, with up to 5 batches. This explains the difference between the 100bp+ DISS metric and the 300bp metric: it’s 300 cycles in total for all that goes into the High Output Cartridge.
There will be an option to include RNA Depletion (Ribosomal RNA, etc.) in the sample, greater than 90% depletion in-house data.
Some data validation. SNP/Indel detection, Stranded Alignment, and gene splicing.
Here an example of cell typing of a group of cell types.
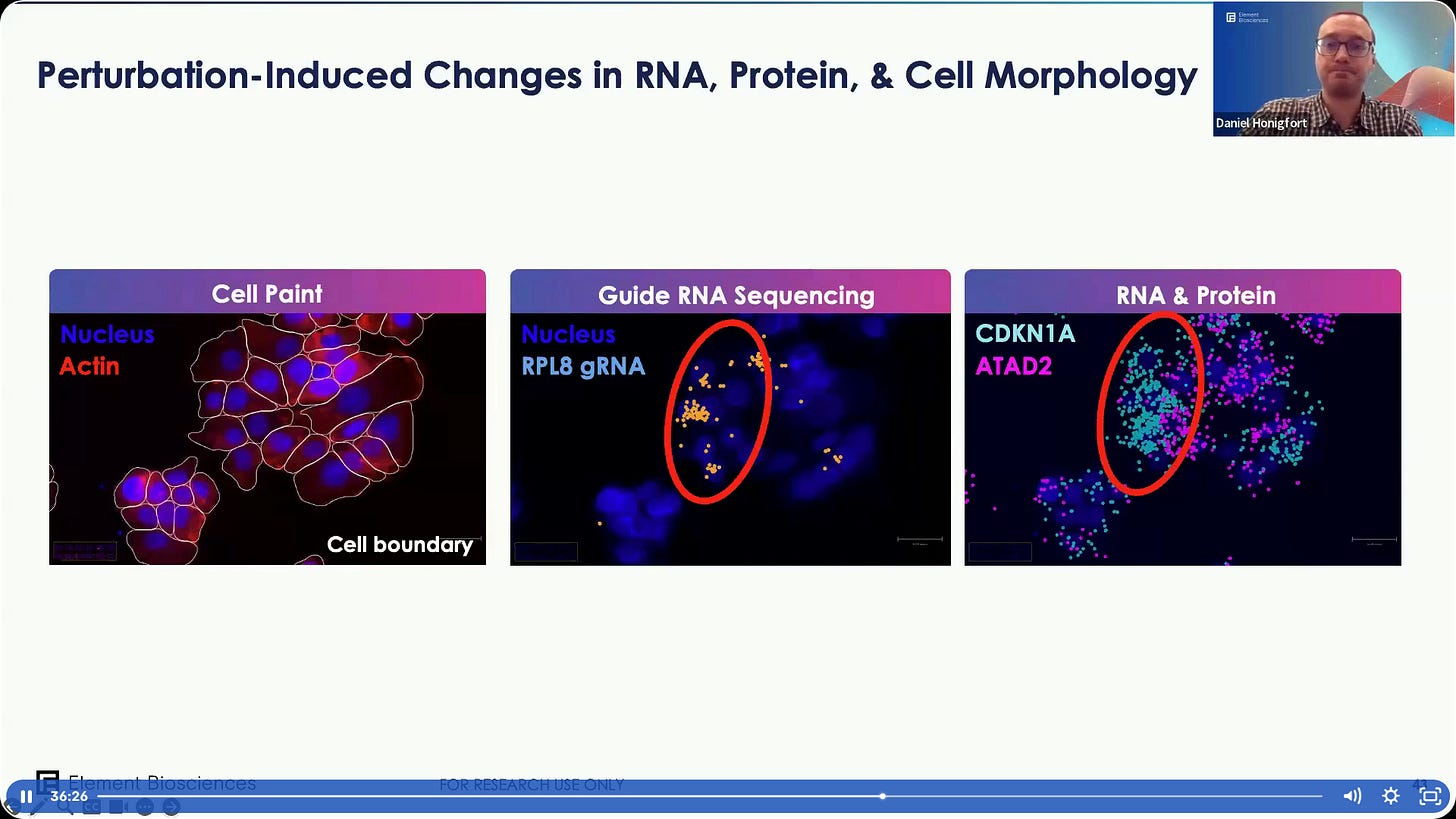
Cell Paint & Protein: Compatibility with DISS. The antibody-based protein labelling can be produced by a Custom Assembly Kit.
Optical Pooled Screens (OPS) is one example that can be used on AVITI24. It can take more than 1 week to do with other methods. Throughput and automation and increasing the omic richness are important considerations.
Difficult to scale CRISPR guide high-plexity when doing whole genome. DISS fixes this limitation.
Example with two types of cells.
Here a collaboration done a while ago with Genentech. Done with 20bp DISS.
This was a 500 gene PERTURB-seq study, each produced more than 2000 cells/gene perturbed, more than enough.
Validation of the assay with known biology. Volcano plots of which perturbed genes cause which phenotypes, such as CALR KO showing reduction in ER intensity in the morphology output.
RNA read-out validation.
More than 1,000 multi-omic features, can be shown in the matrics of Phenotype-genotype correlation.
Here a UMAP clustering of cell-paint only versus all the multi-omics together.
This was presented as a poster in AACR with more details available for download there.
August launch for Teton Atlas.
A program for people to try it out.
The one-well flowcell system is as big as one well in a 6-well plate. For smaller cell types, it can go up to 1 million cells per flowcell, which means it can go up to 2M in the two flowcell AVITI24 runs.